Nuts and Seeds
Food list
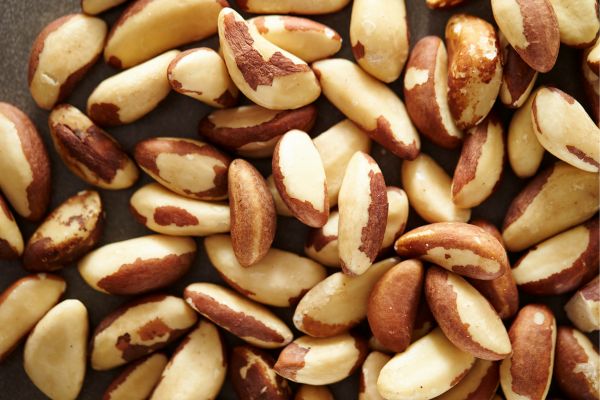

Other names (local names):
Bitter Kola, Orogbo (Yoruba), Aki-inu (Ukwani), and Ugolu (Igbo)
Origin:
Brazil nut is a South American nut known as bitter kola in Nigeria. It bears commercially harvested edible seeds. The fruit and its nutshell- contain the edible nut. As a food, Brazil nuts are notable for their diverse content of micronutrients. They are a good source of healthy fats, proteins, fibre, and antioxidants such as selenium.
Brazil nut oil contains 48% unsaturated fatty acids composed mainly of oleic and linoleic acids, phytosterol, beta-sitosterol, and fat-soluble vitamin E.
Nutritional value and benefits:
S/N | Nutritional content | Quality in 100 gram/ (100 grams of DV) |
1 | Water | 3.48g |
2. | Protein | 14.32g |
3. | Carbohydrates | 12.27g |
4. | Fats | 66.43g |
5. | Dietary fiber | 30% DV |
6. | Thiamin | 54% DV |
7. | Vitamin E | 38% DV |
8. | Magnesium | 106% DV |
9. | Phosphorus | 104% DV |
10. | Manganese | 57% DV |
11. | Zin | 43% DV |
- Brazil nuts provide dietary fiber, which improves blood cholesterol levels and lowers the risk of heart disease, stroke, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.
- The presence of selenium helps to improve people's blood sugar levels. It also improves brain function and plays an essential role in hormone production and regulating thyroid problems.
- The antioxidant properties of Brazil nuts may help reduce inflammation in the body.
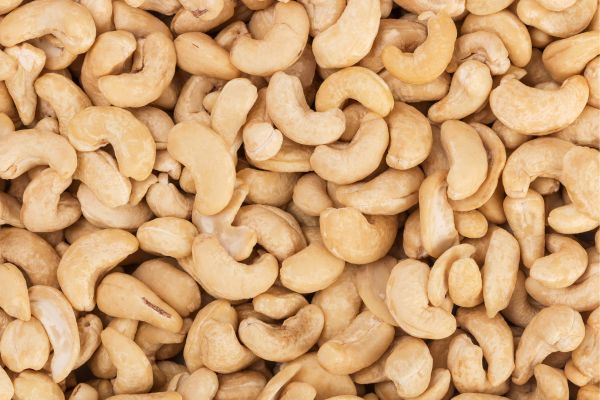

Origin:
The cashew tree is native to South America (Brazil) and produces the cashew seed and apple accessory fruit. The cashew seed is commonly considered a snack nut eaten on its own. It is used in recipes or processed into cashew cheese or cashew butter.
The mature cashew apple can be eaten fresh, cooked in curries, or fermented into vinegar, citric acid, or an alcoholic drink. It also makes preserves, chutneys, and jams in India and Brazil. In many countries, particularly in South America, the cashew apple is used to flavor drinks, both alcoholic and nonalcoholic.
Nutritional value and benefits:
S/N | Nutritional content | Quality in 100% gram/ (100 grams of DV) |
1. | Water | 5% |
2. | Carbohydrates | 30% |
3. | Fats | 44% |
4. | Proteins | 18% |
5. | Dietary fiber | 13% DV |
6. | Copper | 79 - 110% DV |
7. | Manganese | 79 - 110% DV |
8. | Phosphorus | 79 - 110% DV |
9. | Magnesium | 79 - 110% DV |
10. | Thiamin | 32 - 37% DV |
11. | Vitamin B6 | 32 - 37% DV |
12. | Vitamin K | 32 - 37% DV |
The monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids help to decrease LDL ("bad") cholesterol and triglyceride, which help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and heart attack.
Magnesium in cashew nuts also helps in muscle relaxation, neuromuscular transmission, and activity.
Nuts, in general, help maintain a healthy weight. Frequent consumption of nuts helps to reduce the risk of needing to remove the gallbladder.
Cashew nuts contain a high amount of copper, which plays an important role in maintaining collagen and elastin, a major structural component of the body.
The magnesium in cashews is also important for bone formation as it helps assimilate calcium into the bone. Manganese also prevents osteoporosis in combination with calcium and copper
More Information:
For more information, kindly click the following link:
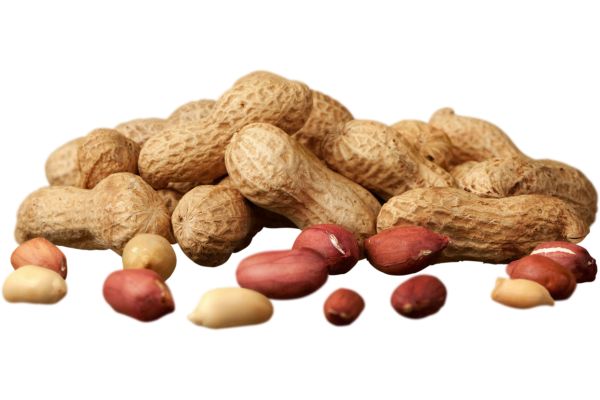

Other names (local names):
Epa (Yoruba), Isagwe (Edo), Ayayaa (Hausa), Opapa (Ibo), Omizaguo (Owan).
Origin:
The peanut or groundnut is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It's native to South America. Dry peanuts can be roasted in the shell or shelled in a home oven if spread out one layer deep in a pan and baked at a temperature of 177 °C (351 °F) for 15 to 20 minutes.
Boiled peanuts are a popular snack in India, China, West Africa, and the southern United States. In the South US, boiled peanuts are often prepared in briny water and sold in street-side stands. Peanuts grow well in southern Mali, Ghana, Nigeria, and Senegal; peanuts are similar in both agricultural and culinary qualities to the Bambara groundnut native to the region, and West Africans have adopted the crop as a staple.
Nutritional value and benefits:
S/N | Nutritional content | Quality in 100 gram/ (100 grams of DV) |
1. | Proteins | 25.8g |
2. | Carbohydrates | 16.13g |
3. | Fiber | 8.5g |
4. | Fats | 24.43g |
5. | Sugars | 4.72g |
- Peanuts contain healthful monounsaturated and polyunsaturated, which help to improve heart health for people with diabetes.
- They are full of healthy fats, proteins, and fiber, which help to maintain a healthy weight and lower the risk of weight gain and obesity.
- They have a low glycemic index, which does not cause a spike in blood sugar levels. Peanuts help to control blood sugar levels because they are relatively low in carbohydrates but high in protein, fat, and fiber.
More Information:
For more information, kindly click the following link:
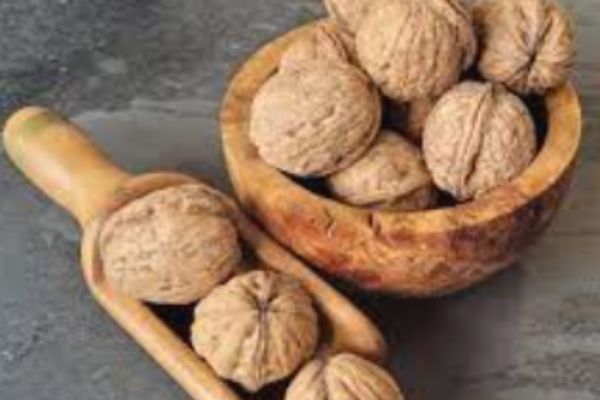

Other names (local names):
Ukpa (Igbo), Ukwa (Igala and Idoma), Gawadi Bairi (Hausa), Awusa or Asala (Yoruba), Ekporo (Efik and Ibibios).
Origin:
A walnut is an edible seed tree native to eastern North America. Walnuts are round, single-seed stone fruits of the walnut tree. They are commonly used for food. During the ripening process, the husk becomes brittle and the shell hard. The shell encloses the kernel or meat, usually in two halves separated by a membranous partition.
The seed kernels – commonly available as shelled walnuts, are enclosed in a brown coat containing antioxidants. The antioxidants protect the oil-rich seed from atmospheric oxygen, preventing rancidity.
S/N | Nutritional content | Quality in 100 gram/ (100 grams of DV) |
1. | Water | 4% |
2. | Carbohydrates | 14% |
3. | Proteins | 14% |
4. | Fats | 65% |
5. | Dietary Fiber | 7% |
Nutritional value and benefits:
- Walnuts are a good source of healthy protein, fats, and fiber, which enhance heart and bone health and help in weight management and other benefits.
- The combination of healthy fats, protein, and fiber in walnuts helps to increase satisfaction and fullness.
- The monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids present in walnuts help to decrease LDL (Bad) cholesterol and triglycerides levels, which helps to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, stroke, and heart attack.
- Walnuts contain copper, which plays an important role in maintaining collagen and elastin, major structural components of the body.
- The presence of manganese in combination with calcium and copper minerals helps prevent osteoporosis.
- Magnesium in walnuts is significant in bone formation and helps absorb calcium into the bone.
More Information:
For more information, kindly click the following link: